Insulated Door & Window Headers
Energy Efficient Door & Window Headers
With a continued focus on energy efficient construction (Green Construction) we are always looking for ways to improve upon residential construction techniques. Insulated door and window headers are one way to improve
on standard framing methods.
Old School Headers
Years ago we used to build door and window headers by creating a sandwich of five pieces of lumber (for a 2×6 wall) consisting of three pieces of 2x material (depth depending on load) and two pieces of 1/2 inch plywood. The idea was to create a header that was 5-1/2 inches thick. The end result was a very strong header with very poor insulating properties.
Insulated Headers
 For one of our current projects we’re using an insulated header. Over the last few years we’ve used several different insulated header types. On the current project we’re using a header that replaces the two layers of 1/2 inch plywood with an inch of DOW polystyrene insulation. The one inch of foam board insulation (XPS) provides approximately an R Value of 4.5 to 5.0. This particular insulated header is on the lower end of what is possible.
For one of our current projects we’re using an insulated header. Over the last few years we’ve used several different insulated header types. On the current project we’re using a header that replaces the two layers of 1/2 inch plywood with an inch of DOW polystyrene insulation. The one inch of foam board insulation (XPS) provides approximately an R Value of 4.5 to 5.0. This particular insulated header is on the lower end of what is possible.
Other versions of the insulated header that we’ve used include headers that use only two outer structural plies (typically upgraded to an LVL due to loading). This increases the insulation in the center to approximately 2-1/2 inches. The insulation can be either XPS for an R value of 11 to 12 or a layer of Polyisocyanurate for an R value of 17 to 20.
(typically upgraded to an LVL due to loading). This increases the insulation in the center to approximately 2-1/2 inches. The insulation can be either XPS for an R value of 11 to 12 or a layer of Polyisocyanurate for an R value of 17 to 20.
This type of insulated header poses some problems. As you can see the header needs to be built with a partial “box” in order to hold it’s shape and retain the insulation. There are two problems with this design:
- Sometimes the loading is too great for the two structural layers.
- The depth of structural layers is limited by the horizontal piece at the bottom, thus further limiting structural capacity.
Insulate Headers For Energy Efficiency
The lesson here is to improve energy efficiency in new home construction by paying attention to small details. Insulated headers might not seem like a big deal but every little bit counts. I’m sure there are even more variations on these examples so if anyone has others please share.
Insulated Header Video
I shot a short video from a job site showing another version of the insulated headers over some windows.




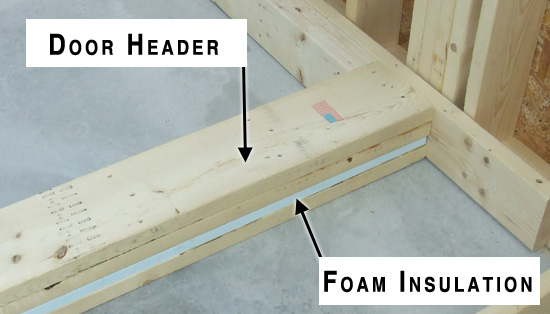














Todd,
Relevant article, especially considering the renewed focus on energy efficiency and green building techniques. When it comes to framing methods, the following is a list of techniques that should be considered when building a new home:
1) Frame 24″ on center rather than 16″ on center.
2) Use less framing and more insulation in corners and wall intersections.
3) Use insulated sheathing under the exterior siding/brick.
Because safety is the top priority in any building project, the local building inspector should be consulted prior to using any of the listed methods.
Hope this helps.
In replay to above suggestion, if you’re framing on 24″ centers, use 2×6 studs rather than 2x4s
Todd, in the video it shows that the insulation is to the inside of the header. Is the load on an exterior wall carried evenly on the whole wall or to one side? Could you move the insulation to the outside plane of the header just to keep the dew point somewhere within the foam? Or did you need the wood for a nailer for the window/door trim?
Jeff – All good questions. We’ve used several variations in the past, on the outside, in the middle and on the inside. In this case the pre-fabricated wall panels came with it on in the inside. That’s fairly standard unless we request it differently because that leaves the “meat” of the header to the outside of the wall so it can be “tied” together with the sheathing.
The dew point is an interesting comment and one I hadn’t given much thought to. From that point of view the exterior position is probably best.
This particular header application has very light loads and we probably could have used a single 2x for additional insulation value.
On larger headers the issue of having nailing surfaces certainly comes into play both inside and out.
Can a six ft wide weight bearing header be built out of 2 – 2 x 8’s with 1/2” styrofoam between them?
Depends on the loading….I’d ask your local building code official or ask at your local lumber yard.